Day 30 of #90daysofdevops
Hey Techies! Welcome to this blog
In this blog, we are going to start the Kubernetes Architecture.
Introduction
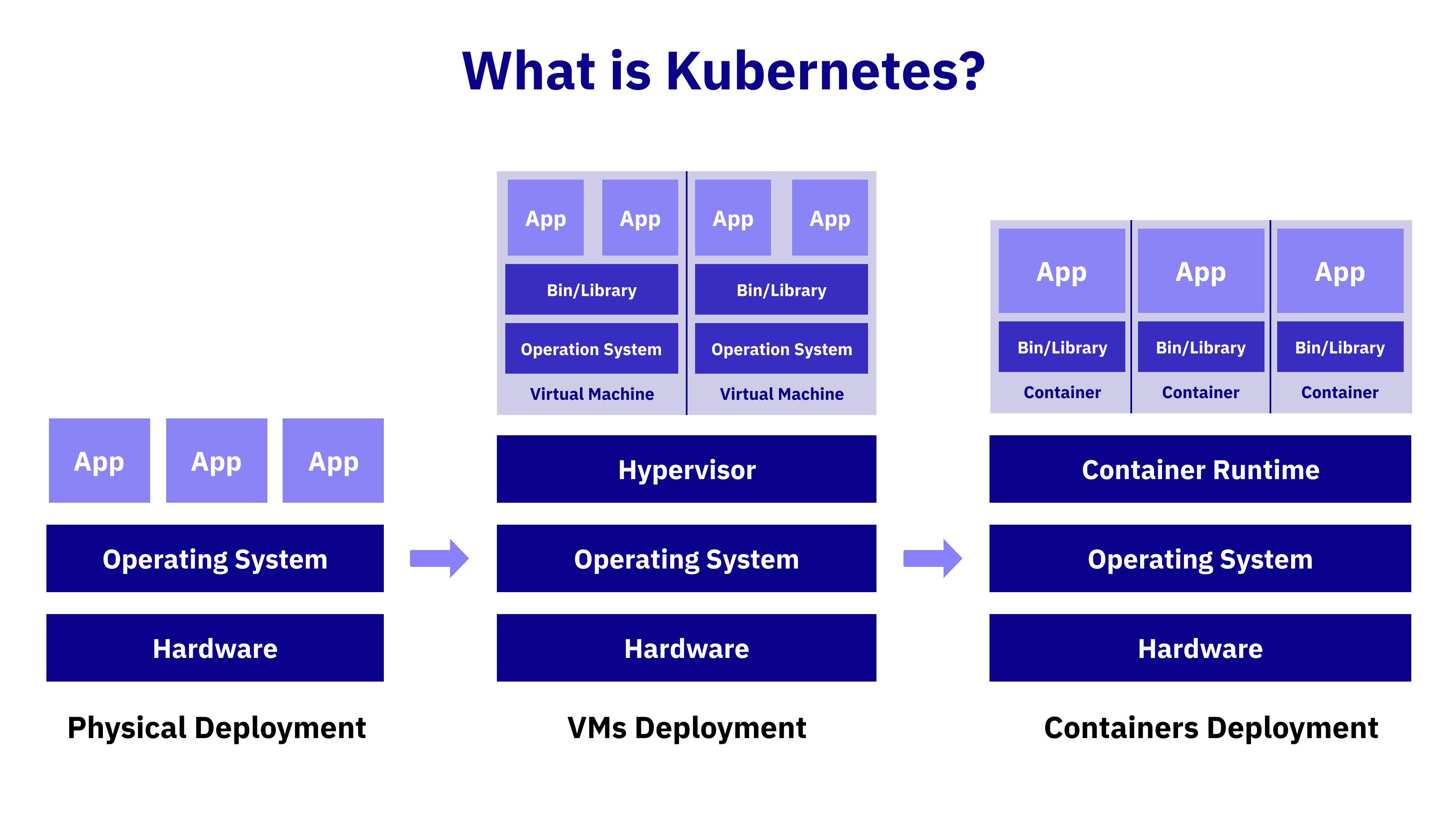
Kubernetes (also known as k8s or “kube”) is an open source container orchestration platform that automates many of the manual processes involved in deploying, managing, and scaling containerized applications.
Supports different infrastructure
Physical servers
VMs Virtual Machines
Clouds
Tasks
What is Kubernetes? Write in your own words and why do we call it k8s?
Kubernetes, or K8s for short, is an open-source container orchestration platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. In simple terms, it helps us efficiently manage and run applications in containers at scale. The name "K8s" originates from the eight letters between 'K' and 's' in the word "Kubernetes."
What are the benefits of using k8s?

Scalability: Kubernetes enables effortless scaling of applications, ensuring they can handle varying workloads.
Resource Efficiency: Efficiently utilize hardware to maximize resource availability.
Container Orchestration: Simplifies the deployment and management of containerized applications.
Auto-Healing: Automatically replaces and reschedules failed containers.
Declarative Configuration: Define the desired state, and Kubernetes ensures the system matches that state.
Explain the architecture of Kubernetes.


API Server - Entry point to K8s cluster.
Controller Manager - Keeps track of whats happening in the cluster.
Scheduler - Ensures pods placement.
etcd - Kubernetes backing store.
Node - Node is a server or virtual machine.
Pod - Pod is the smallest unit in Kubernetes which gives an abstraction over docker container.
Kubernetes architecture comprises several components like nodes, pods, services, and more. Understanding this structure is crucial for effective deployment and management of applications.
Control Plane (Master Node Components)
API Server
This is the "front desk" of Kubernetes. Whenever you want to interact with your cluster, your request goes through the API Server. It validates and processes these requests to the backend components.
etcd
Think of this as the "database" of Kubernetes. It stores all the information about your cluster—what nodes are part of the cluster, what pods are running, what their statuses are, and more.
Scheduler
The "event planner" for your containers. When you ask for a container to be run, the Scheduler decides which machine (Node) in your cluster should run it. It considers resource availability and other constraints while making this decision.
Controller Manager
Imagine a bunch of small robots that continuously monitor the cluster to make sure everything is running smoothly. If something goes wrong (e.g., a Pod crashes), they work to fix it, ensuring the cluster state matches your desired state.
Cloud Controller Manager
This is a specialized component that allows Kubernetes to interact with the underlying cloud provider, like AWS or Azure. It helps in tasks like setting up load balancers and persistent storage.
Worker Node Components :
kubelet
This is the "manager" for each worker node. It ensures all containers on the node are healthy and running as they should be.
kube-proxy
Think of this as the "traffic cop" for network communication either between Pods or from external clients to Pods. It helps in routing the network traffic appropriately.
Container Runtime
This is the software used to run containers. Docker is commonly used, but other runtimes like containerd can also be used.
Other Components :
Pod
The smallest unit in Kubernetes, a Pod is a group of one or more containers. Think of it like an apartment in an apartment building.
Service
This is like a phone directory for Pods. Since Pods can come and go, a Service provides a stable "address" so that other parts of your application can find them.
Volume
This is like an external hard-drive that can be attached to a Pod to store data.
Namespace
A way to divide cluster resources among multiple users or teams. Think of it as having different folders on a shared computer, where each team can only see their own folder.
Ingress
Think of this as the "front door" for external access to your applications, controlling how HTTP and HTTPS traffic should be routed to your services.
What is Control Plane?
The Control Plane in Kubernetes is the central management entity that regulates and controls the entire cluster. It consists of components such as the API server, controller manager, scheduler, and etcd, working together to maintain the desired state of the cluster.
Write the difference between kubectl and kubelet.
kubectl: This command-line tool allows users to interact with the Kubernetes cluster. It facilitates the deployment, inspection, and management of applications within the cluster.
kubelet: Running on each node, kubelet is an agent that ensures containers are running in a Pod. It communicates with the Control Plane and manages containers on the node.
Explain the role of the API server.
API Server: The API server acts as the front-end for the Kubernetes Control Plane. It processes RESTful API requests, validates them, and updates the corresponding objects in etcd, which serves as the cluster's backing store.
That's it! You've just completed the task. 🎉
Thank you so much for taking the time to read till the end! Hope you found this blog informative and helpful.
Feel free to explore more of my content, and don't hesitate to reach out if need any assistance from me or in case of you have any questions.
Happy Learning!